- Using Data Annotations
- Using Custom Data Annotations
- Using Asynchronous validations using Remote
- Using client-side validations using jQuery
For this article, I am using ADO.NET EF with the below table:

Step 1: Open Visual Studio and create a new MVC application, name it as ‘MVC3_Validations’. In this project, add a new Model using ADO.NET EF for the above table.
Step 2: To this project, add a new controller of name ‘TestMasterController.cs’ and use the the following Create methods:
public ActionResult Create()
{
var Test = new TestMaster();
return View(Test);
}
//
// POST: /TestMaster/Create
[HttpPost]
public ActionResult Create(FormCollection collection)
{
try
{
TestMaster test = new TestMaster();
test.TestName = Convert.ToString(collection[0]);
test.Subject = Convert.ToString(collection[1]);
test.TestDate = Convert.ToDateTime(collection[2]);
test.IsApproved = Convert.ToBoolean(collection[3]);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(test.TestName))
{
ModelState.AddModelError("TestName",
"Please Enter the Test Name");
}
if (ModelState.IsValidField("TestDate")
&& DateTime.Now > test.TestDate)
{
ModelState.AddModelError("TestDate",
"Date Must be Greater than current Date");
}
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
objContext.AddToTestMasters(test);
objContext.SaveChanges();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
else
{
return View();
}
}
catch
{
return View();
}
}
The above code uses the if statements to check values entered in the view by the end-user. The errors are registered using ModelState object. Also the IsValidField method of the code verifies whether the model binder was able to assign a value property. This method in the above code is used to check whether the ‘Date’ value entered is parsed or not.
Step 3: Generate Create View from the create method. Set the ValidationSummary method parameter from True to False to view all errors at model level.
Step 4: Run the application, and navigate to the following URL:
hxxp://localhost:1052/TestMaster/Create
Click on the “Create” button and the result will be as shown below:
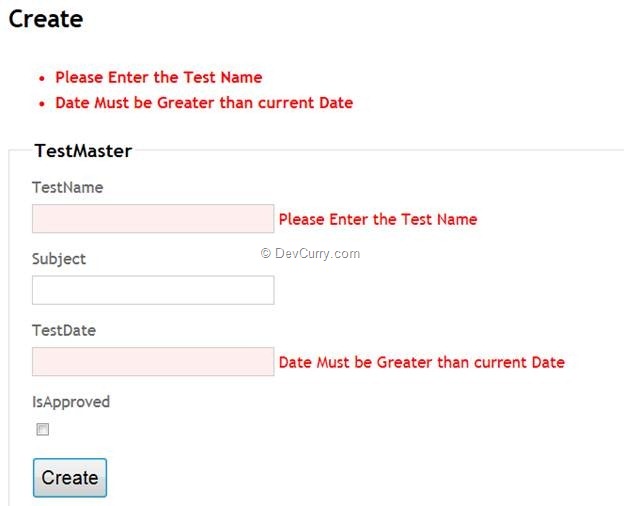
The above UI shows the Validation errors.
Conclusion: Explicit validations are used for implementing more domain specific validation in ASP.NET MVC using controller class.
Download the entire source code

This is quite informative, as being a beginner to ASP.NET. I have just cleared up my basics and now looking for such great tutorials which are easy to follow and to gain something fruitful from it.
ReplyDelete